Tension Springs
Tension springs (also known as extension springs) are spiral coils wrapped tightly together to create tension. When a load is applied to the springs, it spreads the coils apart, which results in resistance of the pulling load. When the load is removed, the coils sling back into their original shape.
Tension springs function as an ideal method to clamp and hold objects, assist in the lifting of heavy objects and disperse the weight of certain loads. The shape, length and thickness of tension springs vary based on their function. Most springs also have hooks, end coils or loops on the end, which are used to attach to an object or component.
Changing the length of the spring, the wire thickness and the coil’s diameter allow users to apply tension springs to an array of applications and loads.
Like most coils and springs, tension springs are constructed from several types of materials to accommodate a particular use. Corrosive elements, temperature and the stress of certain applications determine which type of material manufacturers use to build springs.
Here are a few common uses of tension springs:
- Garage doors
- Trampolines
- Balancing washing machines
- Automotive uses
- Medical devices
- Machinery
A wide selection of springs are available depending on the application and the size of the components. Although they’re cheap and easy to produce and manufacture, extension springs maintain a high level of reliability.
Industrial systems with demanding and extreme environments rely heavily on these springs. Even though they’re available in many variations, the role of all extension springs is to capture and redirect applied force.
Showing 1–9 of 80 results
-
-
-
-
-
-
Clamping & Holding
R20-LTS-3-RT
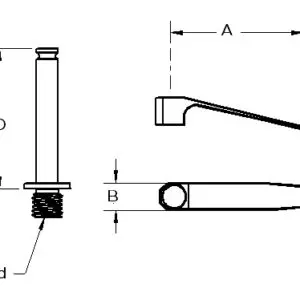
Rubber Tipped Large Tension Spring with 3” Post and 1/4-20 thread
(0 reviews) -
Clamping & Holding
R20-STS-15-RT
Rubber Tipped Small Tension Spring with 1-1/2 Post and 1/4-20 thread
(0 reviews) -
Clamping & Holding
R20-MTS-1-RT
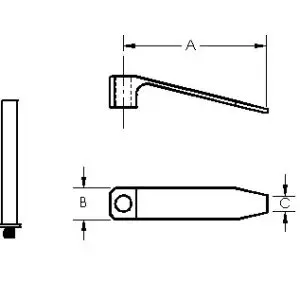
Rubber Tipped Mini Tension Spring with 1” Post and 1/4-20 thread
(0 reviews) -